UNIX 필수 명령어
Linux(UNIX) 필수 명령어
Command completion (auto-comp.)
명령행 완성 기능 (auto-completion)
<Tab>키를 사용
prompt에서 파일, 디렉터리명의 일부만으로 나머지를 완성
prompt에서 명령어 다음에 치는 option, command를 자동 완성
i18n
internationalization
Linux (UNIX) basic commands #0
맨 페이지
man
Linux(UNIX) basic commands #1
파일 관련
path :
pwd, cd, pushd/popd
file data / meta-data :
조회 : ls, file, stat, tree, which, find, locate*
데이터 변경 : cp, mv, rm, mkdir/rmdir, ln, readlink**
메타 변경 : chmod, chown, chgrp, chattr/lsattr
Linux(UNIX) basic commands #2
파일 묶음
archive : tar, cpio
tar는 BSD, cpio는 SysV에서 유래
압축
compress : gzip, bzip2, xz, lz4, zstd***
Linux (UNIX) basic commands #3
Text 관련
editor : vim(vi), nano, emacs
filter : cat(tac), head, tail, less / more, sort, uniq
regex : grep (egrep, fgrep), sed, awk
Job control
jobs, fg, bg, nohup*, disown
Process control
kill, pkill, pgrep, killall
tracing : strace, pmap
Linux(UNIX) basic commands #4
Networking
nc (net cat), curl, wget
w (who)
Disk
df (disk free)
du (disk usage)
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #0
System
uptime, free (/proc/meminfo), smem
process summary : top, htop, atop, sar, saidar
process status : ps, pstree
stat : vmstat, iostat, mpstat, pidstat, statgrab, dstat
hardware : Ishw, lspci, lsusb
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #1
Package
RedHat : rpm, yum, dnf
Debian : dpkg, apt-get/apt-cache/apt-file, apt, aptitude
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #2
Network
status : ss, netstat*
config : nmcli / nmtui, ip, ifconfig/route*, iw/iwconfig
arp, dig, nslookup*
ssh, sftp, scp, ssh-copy-id
packet : tcpdump, wireshark, tshark
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #3
Files
open files : Isof, fuser
Kernel
커널 파라미터 : sysctl
커널 모듈 : Ismod, modprobe, rmmod
Firewall
iptables, ip6tables
firewall-cmd, ufw
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #4
Disks
fdisk, cfdisk, sfdisk, fixparts, flock,
parted, gdisk, cgdisk, sgdisk
mkfs, fsck
mount, lsblk, blkid
grubby, grub2-install, grub2-mkconfig, grub2-editenv
lvs, vgs, pvs
udisksctl
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #5
Security
ulimit
visudo
sestatus, getsebool / setsebool, getenforce / setenforce
abrt
User
useradd, groupadd, usermod, groupdel, chgrp, newgrp
passwd, chpasswd, gpasswd
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #6
Service
init, service, chkconfig, ntsysv, update-rc
systemctl
Performance
tuned-adm
perf
pcp
Locale
locale, localectl (update locale)
Linux (UNIX) admin commands #7
Alternatives
update-alternatives
Linux (UNIX) dev. commands #0
Compiler
gcc, g++, clang
Debugging, tracing
gdb, strace, coredumpctl
Tools
make, maven, graddle
git
Linux (UNIX) dev. commands #1
python
python2, pip
python3, pip3
Obsolete commands #1
리눅스 명령어는 세대에 따라 다르다.
필수 명령어, 개념
pwd, cd, ls, cp, mv, rm, mkdir, ln, find, chmod, ssh
vim
필수 탑재 개념
UNIX account
UNIX ownership : user, group
UNIX file mode : 권한 (rwx), numeric / symbolic
Link : hard link, symbolic link
Path : absolute path, relative path, CWD(Current Working Directory)
Shell
File관련 명령어
pwd, cd
ls, mkdir/rmdir
cp, mv, rm
chmod, chown, chgrp
Path : pwd, cd
pwd - print working directory
cd - change directory
Directory : 절대 / 상대 경로
absolute path (절대 경로) = 줄여서 abs-path라고 함
root directory ( / )를 시작으로 하는 경로
relative path (상대 경로)
현재 디렉토리 ( . )를 시작으로 하는 경로.
Practice : path
file : ls
ls - list file
ls [-altriRr] [파일명]
file : UNIX file mode
file : UNIX file mode : octal mode
Octal mode : 8진수로 표기되는 UNIX file mode
file : UNIX file mode bit
directory인 경우: readable file list, writable file, accessible
directory : mkdir, rmdir
mkdir - make directory
mkdir [-p] <directory name>
rmdir - remove directory
rmdir [-p] <directory name>
디렉토리가 비어있는 경우에만 삭제 가능
rmdir 대신에 rm -rf
UNIX file mode bit
file : UNIX file mode bit
file : cp, mv, rm
cp : copy
mv : move, rename
rm : remove
!$ : 가장 마지막의 타이핑 쳤던 것의 뒷부분을 copy해라
file : chmod
chmod (change mode)
file : chown, chgrp
chown, chgrp - change owner / group
root 유저만 가능
chattr - change attribute
리눅스 파일 시스템의 커스텀 속성 변경
File 관련 명령어
file 정보 : file, stat
touch
find
file
file <file>
파일의 타입 확인
magic 데이터
stat
stat [option] <file>
status of file
file의 meta data를 출력한다.
file : stat
<ALT-.> : 가장 마지막의 타이핑 쳤던 것의 가장 마지막 인수 명령을 copy해라
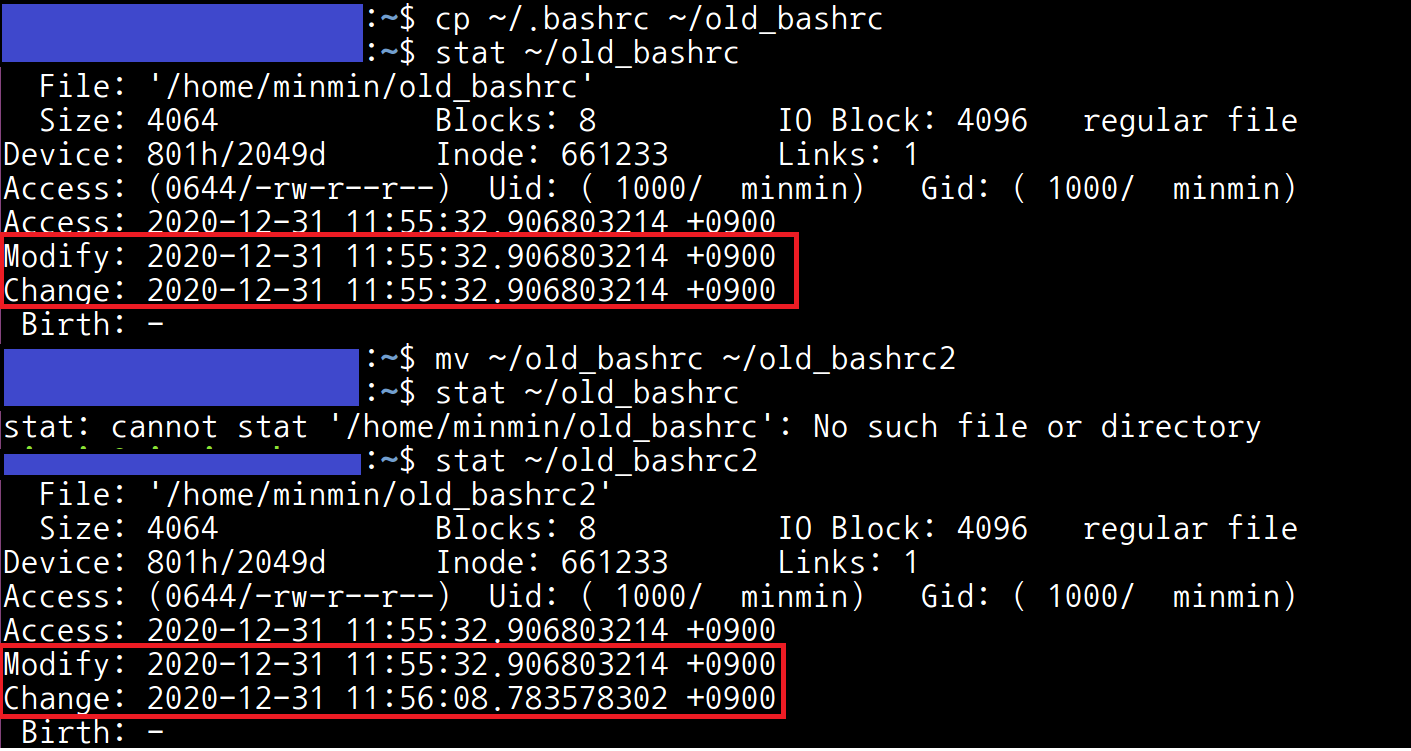
예제 파일 실행 시, 파일 이름이 변하므로 Change가 변한다.
touch
touch <file>
파일의 메타 정보 업데이트
find
find
find directory [expression]
검색 후 작업지시
find . . . . -exec 명령어 \;
find . . . . -exec 명령어 \+
\; 과 \+ 의 차이는?
\;는 명령어가 매번 찾을 때마다 하나씩 실행, \+ 다 더해서 하나로 실행
Practice #4
stdio / archiving and compression
stdio (표준 입출력) 기초
stdio (standard input/output)
pipe, redirection
stdio (표준입출력)
stdio - Standard Input / Output
파일 채널 (file channel)
파일에 입출력을 하기 위한 메타 정보를 가지는 객체
파일서술자 (file descriptor) == 파일기술자
파일 채널에게 붙여진 유일한 식별자(identifier), 숫자로 명명
fd (file descriptor)
file descriptor : 파일 서술자, 파일 기술자
PIPE
프로세스 사이에 통신으로 사용
PIPE의 종류 2가지
anonymous pipe
temporary
named pipe
persistency
PIPE : anonymous pipe
프로세스들의 직렬 연결
명령행에서 vertical bar ( | )로 사용
wc : word count
-l 옵션 사용시 line 수를 카운트
PIPE : 파이프의 종류
anonymous pipe (nameless pipe, unnamed pipe)
named pipe
mkfifo 명령을 사용하여 생성
redirection (방향 재지정)
채널의 방향을 다른 곳으로 연결
A > B : A의 stdout을 파일 B로 연결
A < B : A의 stdin을 파일 B로 연결
A >> B : 방향을 > 와 같고, 추가하는 모드
cat
stdout과 파일을 자유롭게 연결해주는 기본 필터
아카이브, 압축 명령어
tar, cpio
gzip, xz, bzip2, zstd
archive (보관용 묶음), compress (압축)
UNIX계열은 여러 파일을 묶는 작업과 압축이 분리되어있음
아카이브 유틸 : tar (tape archive, BSD), cpio (SysV)
압축 유틸 : gzip, bzip2, xz, zstd, lz4
압축률은 xz > bzip2 > zstd > gzip > lz4 순이다.
아카이빙 : tar
tar [ctxv] [f archive-file] files . . .
$ tar c *.c > arc_c.tar == $ tar cf arc_c.tar *.c
압축 : 프로그램의 발전
압축 : 종류
압축 알고리즘 테스트
압축 : gzip
gzip [-cdflrv] <file ...>
압축 : bzip2, XZ
bzip2 [-cdfv] <file ...>
압축 : zstd
zstd [OPTIONS] [-|input-file] [-o output-file]
Practice : tar, gzip
verbose 옵션의 문제
verbose는 화면 출력으로 인해 I/O delay가 증가
압축 : tar extensions
Practice : tar, compression
git clone
htop-dev/htop
htop - an interactive process viewer. Contribute to htop-dev/htop development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
link
File 관련 명령어
link : hard link, symbolic link
i-node
which
readlink, canonical path
file : In (link)
ln - make links
하드 링크 (hard link)
심볼릭 링크(symbolic link) : 축약시 symlink 라고 함. (-s 옵션 사용)
i-node
파일의 메타 정보 및 관리용 객체
ln (link) : hard vs symbolic
file : In (link) : hard
hard link인 hardlink.txt와 hello.txt 중에 어느 파일이 원본인가?
둘다 원본이다.
hello.txt를 지워보면? 어떤 변화가 생기는가?
file : In (link) : symbolic
which
PATH에 존재하는 파일을 검색
readlink
Symlink가 여러 단계로 가리키는 파일이 있을 수 있다.
그래서 symlink의 canonical path를 따라가는 기능이 있다.
readlink -f <symlink>
canonical path를 따라가면서 마지막 링크를 제외한 모든 링크가 존재할 때 성공
readlink -e <symlink>
canonical path를 따라가면서 모든 링크가 존재할 때 성공
canonicalization
canonical이란 컴퓨팅 환경에서 실체를 가지는 standard, official의 의미를 가진다.
즉 상대적인 의미를 해석한 뒤 standard, official의 대상을 한정하는 것을 canonicalize라고 표현한다.
Practice: symlinks
Practice: canonicalization
Symlink를 사용하는 예 #1
Symlink를 사용하는 예 #2
process
Process 관련 명령어
ps, pgrep
kill, pkill
Job control
top
ps : process status
ps는 기본적으로 현재 세션의 프로세스들을 보여준다.
ps : all processes
e-
Select all processes.
-a
Select all processes except both session leaders and processes not associated with a terminal.
ps : full-format
-f
ps : long-format
-l
ps : all, long, full
ps : BSD, SysV style
ps는 UNIX 표준화 후 2가지 옵션을 지원하기 시작했다.
man ps 명령으로 확인해보자.
ps : man
Practice : ps
Tip! ps를 통해 실력자를 알아보는 방법
Process control #1
kill : send signal
UNIX Signal (기초)
kill
실제로는 프로세스에 시그널을 send하는 기능이다.
kill -l 명령으로 시그널 리스트 확인 가능
1~31 : UNIX signal (UNIX traditional siganl) 프로세스 제어 용도
34 ~ : real time signal 통신 용도
kill : UNIX signals
대표적인 유닉스 시그널
SIGHUP : Hang Up
SIGINT : Interrupt <CTRL-C>
SIGQUIT : Quit <CTRL-\>
SIGKILL : kill
SIGSEGV : Segment violation
SIGTERM : Terminate
SIGTSTP : Temporary Stop <CTRL-Z>
Practice : ps, kill
Process control
Job control : fg, bg
foreground, background 정의
session, controlling terminal
job control : fore/back-ground process
fore-ground process
현재 session에서 제어 터미널(controlling terminal)을 가진 프로세스 *
back-ground process
현재 session에서 제어 터미널(controlling terminal)을 잃어버린 프로세스 *
CTRL-Z
SIGTSTP(Signal - Temporary Stop) 시그널을 fore-ground 프로세스에 전달
작동 :잠시 정지시킴 = 결과적으로 back-ground에 Stopped 상태로...
job control : session
세션 (session)
세션은 멀티유저 시스템에서 통신 객체(seat or remote)를 구별하기 위함.
job control : controlling terminal
제어터미널(controlling terminal)
사용자의 제어(e.g. 키보드 입력)를 받는 터미널 장치
하나의 session에서 fore-ground process는 최대 몇 개까지 가능한가?
1개
job control : controlling terminal
제어 터미널 규격
pts/# : UNIX98 Pseudo terminal system
tty# : console terminal
Session에서 제어 터미널을 가지지 않는 경우에는 ps 의 TTY 필드에 ? 로 나타난다.
ps -e | less 로 확인
Session, ProsessGroup
Process Group
Process group leader : ProcessGroup ID == PID
Session, ProcessGrp, Process
Tip!
job control : interrupt key
CTRL-C
SIGINT(Interrupt Signal) 시그널을 fore-ground 프로세스에 전달
CTRL-\
SIGQUIT(Quit Signal) 시그널을 fore-ground 프로세스에 전달
job control : commands
jobs
stoped, back-ground process 의 리스트 출력
fg %#
#에는 jobs의 작업 번호
bg %#
정지된 백그라운드 프로세스를 back-ground에서 running 상태로 변경
command &
command를 back-ground에서 running 상태로 실행시킴
Practice : job control
Quiz
'자율주행 데브코스 > WEEK02 - LINUX' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DAY03. vim editor (0) | 2021.01.01 |
|---|---|
| DAY01. Linux 기초 (0) | 2020.12.29 |
| DAY01. Linux 역사, 배포판 (0) | 2020.12.29 |